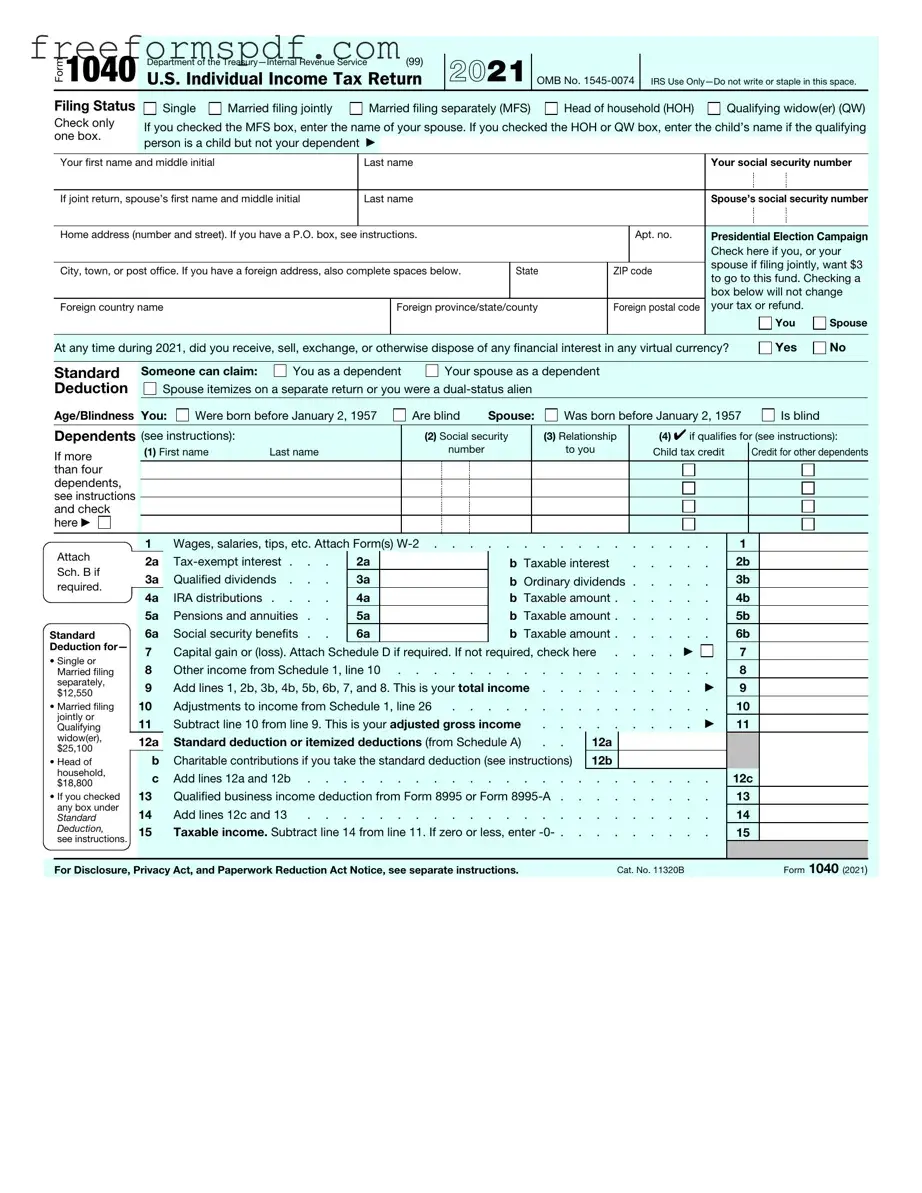
Fill in a Valid IRS 1040 Template
Common mistakes
-
Incorrect Personal Information: Many individuals fail to double-check their name, Social Security number, and address. Even a small typo can lead to significant delays in processing.
-
Filing Status Errors: Selecting the wrong filing status can affect your tax rate and eligibility for certain credits. Review your options carefully.
-
Math Mistakes: Simple addition or subtraction errors can lead to inaccurate calculations of your taxable income or refund. Always verify your math.
-
Missing Signatures: Forgetting to sign the form is a common oversight. An unsigned return is considered invalid and may result in penalties.
-
Neglecting to Attach Required Forms: Certain deductions and credits require additional forms. Failing to include these can delay processing or result in denied claims.
-
Incorrect Bank Information: If you choose direct deposit, ensure your bank account and routing numbers are correct. Mistakes can lead to lost refunds.
-
Missing Deadlines: Not submitting your return on time can incur penalties and interest. Mark your calendar and file early to avoid last-minute issues.
Learn More on This Form
-
What is the IRS 1040 form?
The IRS 1040 form is the standard individual income tax return form used by U.S. taxpayers. It is used to report income, calculate taxes owed, and claim refunds or credits. Most people will need to fill out this form when filing their annual taxes.
-
Who needs to file a 1040 form?
Generally, anyone who earns income in the U.S. must file a 1040 form. This includes employees, self-employed individuals, and those receiving other types of income. Specific income thresholds apply, which can vary based on your filing status, age, and whether you can be claimed as a dependent.
-
What information do I need to complete the 1040 form?
To complete the 1040 form, you will need personal information such as your Social Security number, filing status, and details about your dependents. Additionally, you must report all sources of income, such as wages, dividends, and interest. Information about deductions and credits is also necessary to accurately calculate your tax liability.
-
What are the differences between the 1040, 1040A, and 1040EZ forms?
The 1040 form is the most comprehensive option and allows for various deductions and credits. The 1040A is a simplified version that is used for taxpayers with straightforward financial situations. The 1040EZ is the simplest form, designed for single filers or couples without dependents, who earn less than a specified amount and do not claim any adjustments to income.
-
When is the deadline for filing the 1040 form?
The deadline for filing the 1040 form is typically April 15 each year. If this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline may be extended. Taxpayers can also request an extension, giving them until October 15 to file, but any taxes owed must still be paid by the original deadline to avoid penalties.
-
Can I file my 1040 form electronically?
Yes, you can file your 1040 form electronically using various tax software programs or through the IRS website. E-filing is often faster and more convenient, and it can lead to quicker refunds. The IRS also offers free e-filing options for those who meet certain income requirements.
-
What should I do if I make a mistake on my 1040 form?
If you discover a mistake after filing your 1040 form, you can correct it by submitting an amended return using Form 1040-X. This form allows you to make changes to your original return, whether it’s to correct income, deductions, or filing status. Be sure to file the amendment as soon as possible to avoid potential penalties.
Misconceptions
The IRS 1040 form is a crucial document for individual taxpayers in the United States, yet many misunderstand its purpose and requirements. Here are eight common misconceptions about the 1040 form:
- Everyone must file a 1040 form. Not all individuals are required to file. If your income is below a certain threshold, you may not need to submit a tax return.
- Filing a 1040 guarantees a refund. While many people receive refunds, filing does not ensure one. Your tax situation will determine whether you owe money or receive a refund.
- All income must be reported on the 1040. Certain types of income, like some gifts or inheritances, do not need to be reported. However, most earned income does need to be included.
- Filing late results in immediate penalties. While there can be penalties for late filing, the IRS may grant extensions under certain circumstances, allowing additional time without immediate penalties.
- Only employees need to file a 1040. Self-employed individuals, freelancers, and those with investment income also need to file a 1040, regardless of their employment status.
- Tax software is always necessary for filing. While tax software can simplify the process, many individuals still choose to file their taxes manually using paper forms.
- Once filed, a 1040 cannot be changed. If you discover an error after filing, you can amend your return using Form 1040-X to correct the information.
- Filing electronically is always safer. While electronic filing can be secure, it is essential to ensure that you are using reputable software and following best practices for online security.
Understanding these misconceptions can help taxpayers navigate the filing process more effectively and avoid potential pitfalls.
Browse More Forms
Coat of Armor - A visual narrative of achievements and lineage.
Florida Family Law Financial Affidavit Short Form - This form is specifically designed for use in family law cases, providing a snapshot of your finances.
In addition to the essential information about the NYCERS F266 form, prospective applicants can find helpful resources, such as the NY Templates, to guide them through the application process and ensure the proper completion of their retirement benefit applications.
Fedx Freight - It underscores the importance of ensuring proper packaging to facilitate safe transportation.